How Amazon Achieved Profitability
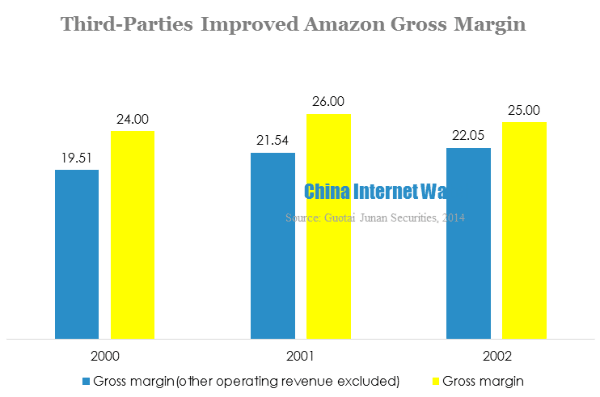
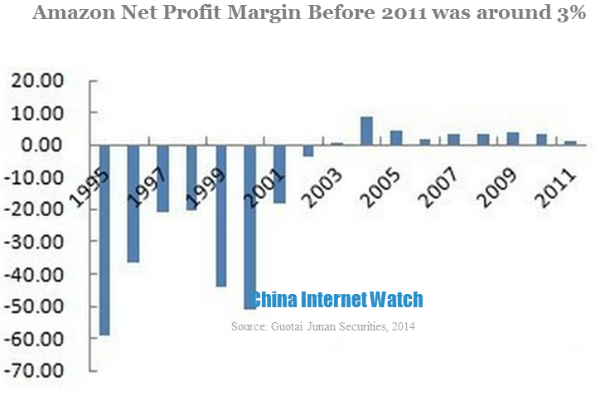
Guotai Junan Securities did a profit analysis for Amazon, it found out that if other operating revenue was excluded, the gross margin would drop by 3 to 4 percentage points. Amazon’s net profit margin was around 3% before 2011, which indicated that if other operating revenue excluded, the company’s net profit margin was zero. In the recent years, Amazon’s third parties revenue kept growing, probably accounted for 30%. Therefore, if third parties commission and advertising revenue excluded, Amazon’s net profit margin would be negative value.
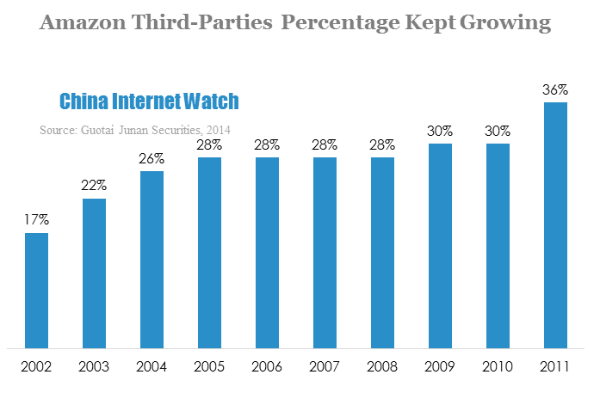
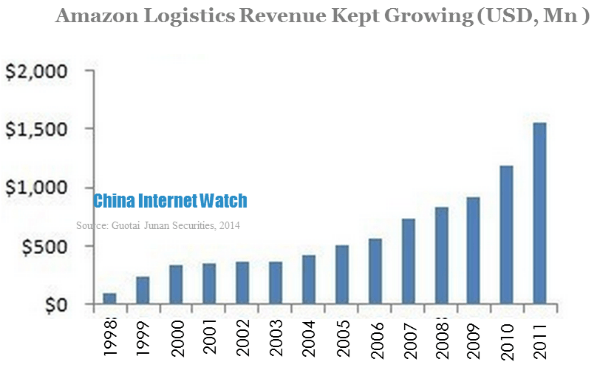
According to the analysis, Amazon B2C platform brought traffic to the site, while third-party platforms, warehousing, cloud service and advertising were the key drivers of revenue.
Jingdong Compared with Amazon
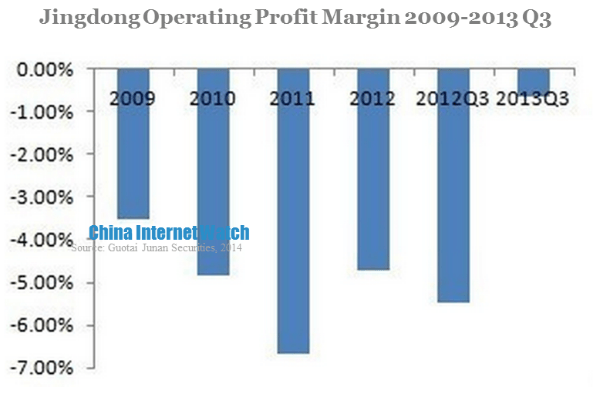
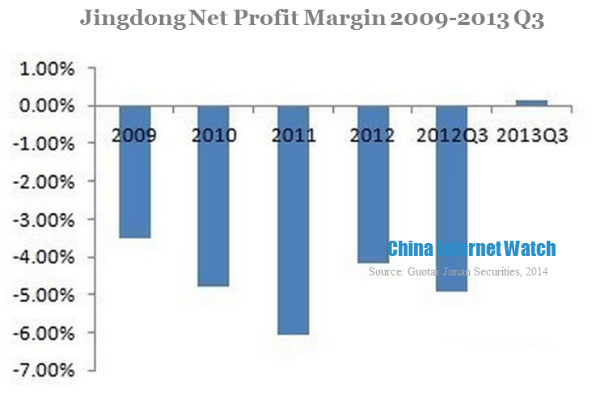
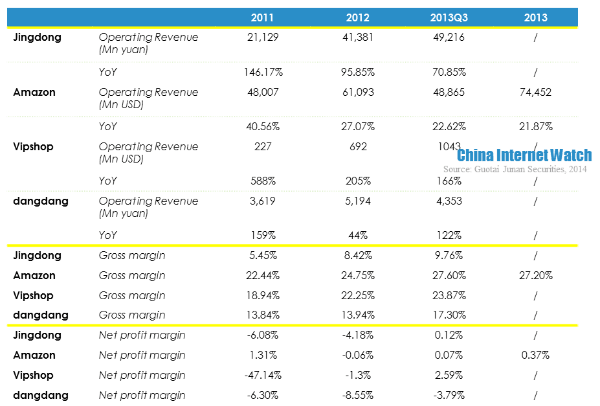
Jingdong’s revenue in 2013 was approximately one sixths of Amazon, and its loss was narrowing. In the first three quarters of 2013, Jingdong realized 60 million yuan (USD 9.79 million) net profit and its operating profit margin was -0.64% which was 4.82 percentage points less than that of 2012. Its net profit margin was 0.12%, achieving profitability for the first time.
In Q3 2013, Jingdong ranked the second in China B2C market, with 18.3% share. And Jingdong led independent sale market with 39% share.
Why did Jingdong achieve profitability?
In the first three quarters, Jingdong’s operating revenue was -316 million yuan (USD 51.55 million) and its net profit was 60 million yuan (USD 9.79 million). By analyzing Jingdong’s financial statements, we could discover that interest income was 222 million yuan (USD 36.22 million), other operating income was 164 million yuan (USD 26.75 million). Interest income and other operating income added up to 386 million yuan (USD 62.97 million), deducted 10 million yuan (USD 1.63 million) tax and plus -316 million yuan (USD 51.55 million) which was equaled to net profit.
Therefore, the source of Jingdong’s profit came from interest income, government subsidies and tax refund. B2C was still at a loss, it was similar to Amazon but Jingdong’s profit was not sustainable.
How did Jingdong’s negative operating revenue narrow down?
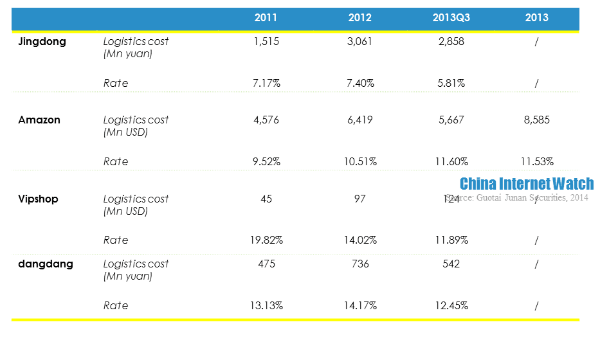
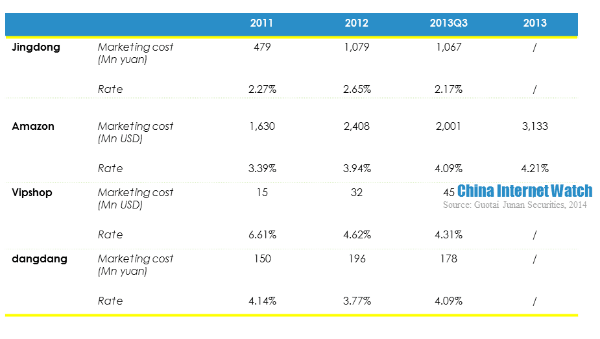
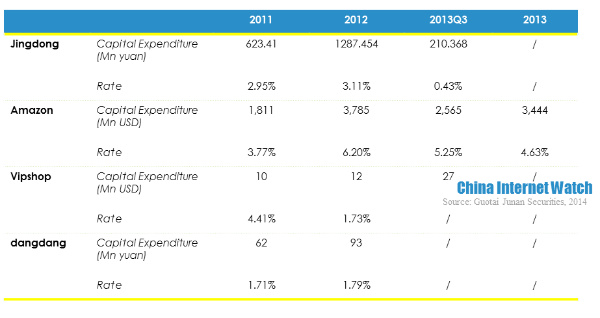
The main reasons for Jingdong’s negative operating revenue narrowing were the decrease of capital expenditure and logistics cost rate and marketing cost. Jingdong’s capital expenditure was merely 210 million yuan (USD 34.26 million) in the first three quarters of 2013, while the capital expenditure in 2012 reached 1.287 billion yuan (USD 209.96 million). At the same time, logistics and marketing costs together dropped 2.74 percentage points. Considering these factors, Jingdong’s profitability did not turn good in 2013.
Differences between Jingdong and Amazon
- Jingdong’s capital expenditure was far less than Amazon’s. The reason why Amazon’s net profit margin decreased since 2011 was mainly because of capital expenditure increasing. In 2011, Amazon’s capital expenditure was 1.811 billion yuan (USD 295.44 million), with an 85% YoY increase. It increased 109% the next year, reaching 3.785 billion yuan (USD 617.48 million). Though the capital expenditure in 2013 decreased slightly, it still maintained as 3.444 billion yuan (USD 561.85 million). Amazon’s large amount capital expenditure mainly used to build storage centers, which became one of main sources of income.
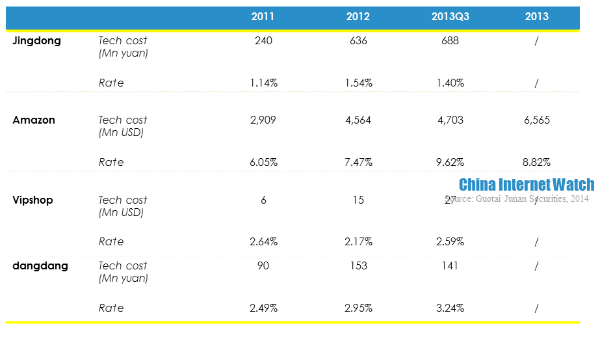
- Jingdong had relatively lower technology investment. In the first three quarters of 2013, Jingdong’s technology investment was only 688 million yuan (USD 112.24 million), with 1.4% rate. While Amazon invested 4.703 billion yuan (USD 767.24 million) in the same period, with 9.62% rate. Besides, Amazon’s technology investment tended to increase prominently. It mainly invested in cloud service platform, which was another secret of Amazon’s profitability and better use experience.
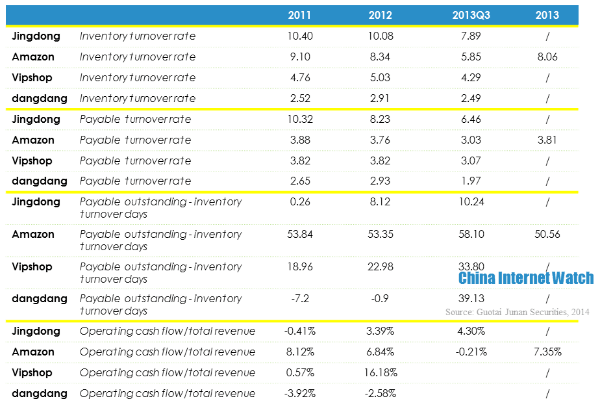
Jingdong’s gross net profit was lower than Amazon, Vipshop and dangdang because of product mix. Jingdong’s logistics cost rate, marketing cost rate, and technology cost rate were all lower than the other three competitors, but it had higher inventory turnover rate which was 12.5 times in 2011. But it tended to drop slightly in the recent two years. Besides, it was also found that the difference between days payable outstanding and inventory turnover days was growing, which means Jingdong took up suppliers’ payments for goods increasingly longer.
In the first three quarters of 2013, Jingdong’s cash and equivalents was 8.812 billion yuan (USD 1.44 billion) and its accounts payable was 10.678 billion yuan (USD 1.74 billion). When restricted cash of 999 million yuan (USD 162.97 million) considered, the difference still was 867 million yuan (USD 141.44 million). It could only be paid off by getting short-term investment of 3.468 billion yuan (USD 565.77 million) back.
Financial indicators of Jingdong, Amazon, Vipshop and dangdang.