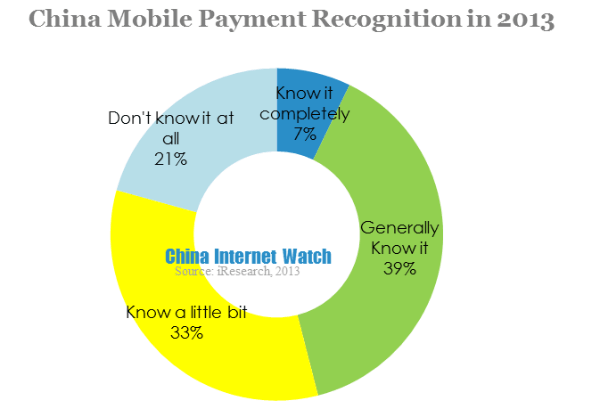
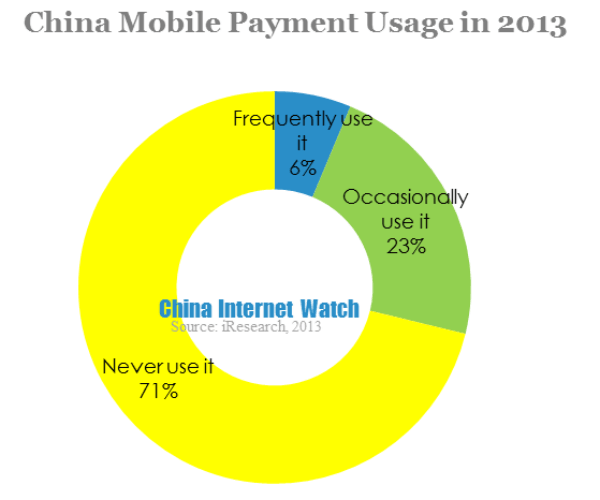
According to iResearch report on China mobile payment user behavior in 2013, in the aspects of mobile payment recognition, only 20.7% of Chinese users knew nothing about mobile payment. Over 70% of users had a certain knowledge of mobile payment. At the same time, 71.2% of users haven’t used mobile payment before, frequently users only accounted for 6.3%.
This high recognition and low usage rate was in accordance with mobile payment growing stage in China market, with mobile internet development and consumer habits changing, mobile payment would enter its fast developing stage. China mobile netizen’s recognition for mobile payment would keep growing, and mobile payment usage rate would increase largely.
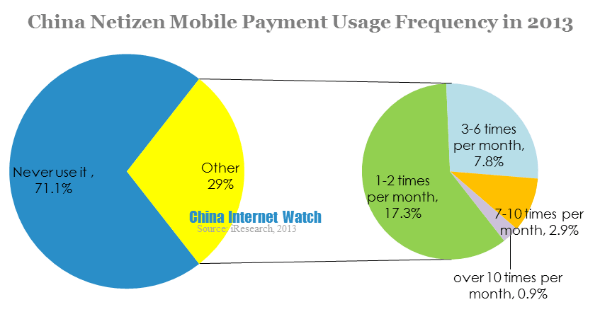
Data showed that 17.3% of consumers used mobile payment 1-2 times per month, nearly 8% of consumers used it 3-6 times per month. While only 0.9% used more than 10 times per month. Mobile payment usage low frequency was because offline shopping remained the dominance, though online shopping grew fast in certain user groups.
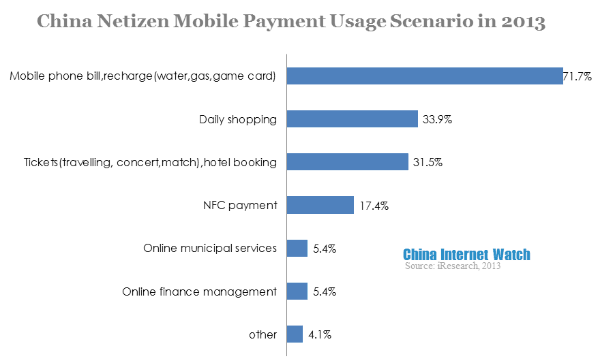
71.7% of respondents would use mobile payment for phone bill and recharges. 33.9% said they would use mobile payment for daily shopping and 31.5% in tickets booking. Phone bill and recharges were related to mobile, therefore it’s natural for consumers to use mobile payment. Chinese netizen’s shopping habits hadn’t transferred from PC end to mobile end, mobile payment could not replace PC end payment methods in daily shopping and tickets booking. NFC payment would increase consumers’ device update cost, so it was not popular.
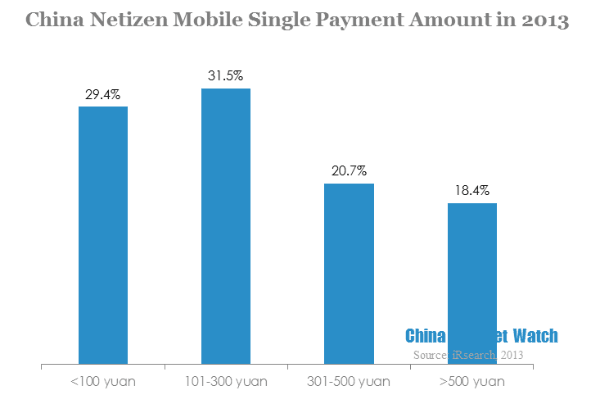
29.4% of China mobile netizen were willing to pay for 101-300 yuan (USD 16.52 to 49.06) in a single transaction, 39.1% would pay for over 300 yuan (USD 49.06). Mobile payment users were mainly young people, their incoming limited their spending. Besides, most mobile payment transactions were phone bills and recharges. Considering the money security, most users dared not to invest a large sum in mobile end.
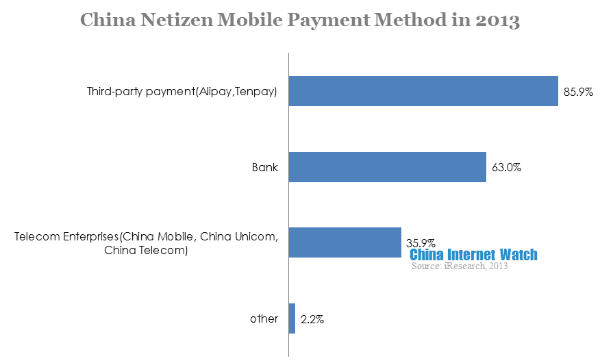
85.9% of users would choose third-party payment enterprises, banks were their second option. Third-party payment enterprises had built up large user base in PC end, their mobile end payment attracted their PC end users and attained user loyalty. Similarly, banks launched their mobile apps one after another, and its penetration rate improved for its credibility and security. China telecom enterprises’ market reactions were too slow and their products were replaceable.
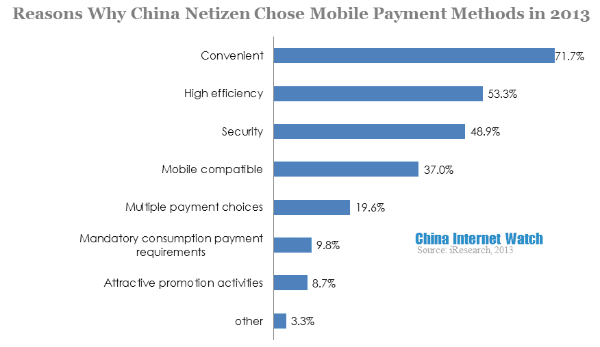
Data showed that convenience, efficiency and security were the top three reasons why consumers chose payment enterprises. Alipay and ICBC bank had accumulated many years of experience and formed competitive advantages.
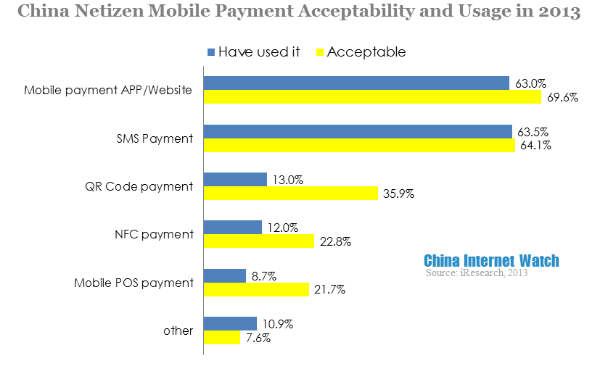
Chinese mobile netizen had the highest acceptance for mobile payment app/website and SMS payment. The differences between acceptability and usage rate in QR code payment, NFC payment and mobile POS payment were quite big. Consumers had accepted and used mobile payment app/website and SMS payment, as for QR code payment, NFC payment and mobile POS payment, they were not popular yet therefore their acceptability and usage rate were both very low.
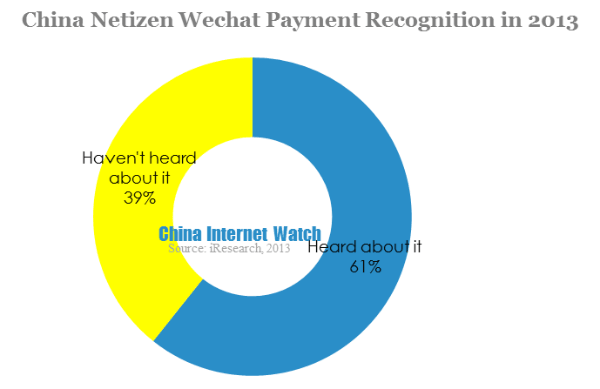
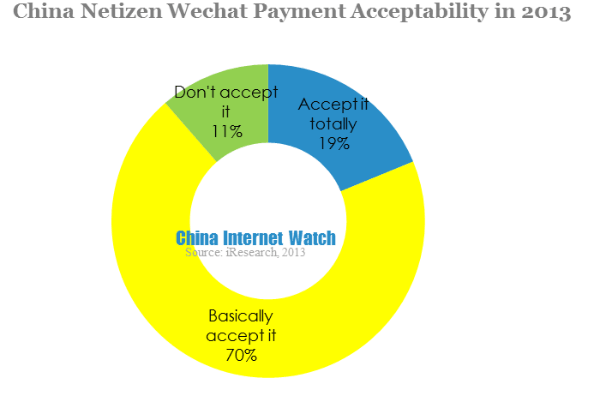
60.7% of mobile netizen had heard about Wechat payment, and 69.8% said they basically accept Wechat payment while 11.4% wouldn’t accept it. The launch of Wechat 5.0 gained wide recognition of Wechat payment, what’s more, Wechat had a large registered user base and it’s easier for Wechat payment to be accepted.
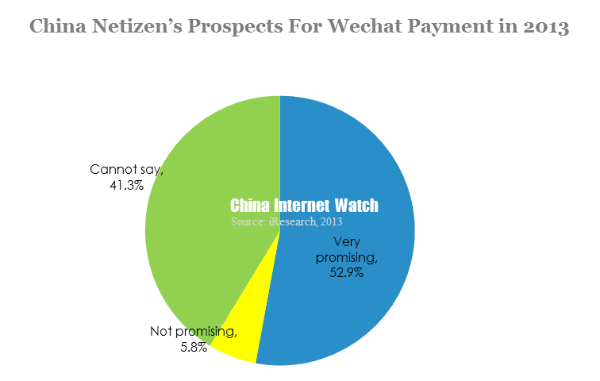
52.9% of mobile netizen believed Wechat payment would have a very promising future, while 5.8% didn’t agree. Still, about 40% hold wait and see relatively conservative attitude, because the benefits of Wechat payment still needed to be proved.
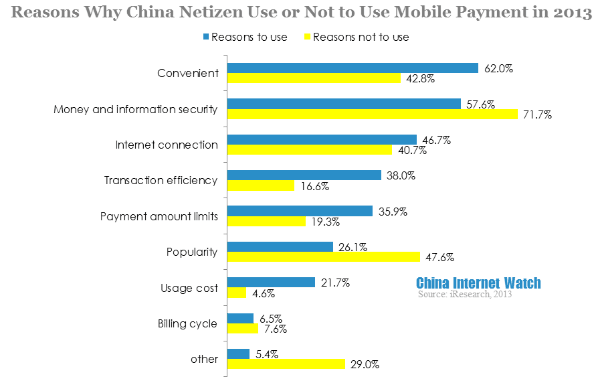
The difference of mobile payment was its convenience, 62% of mobile netizen used mobile payment for its convenience. However, users different recognition for mobile payment security may cause by diversed individual experience.
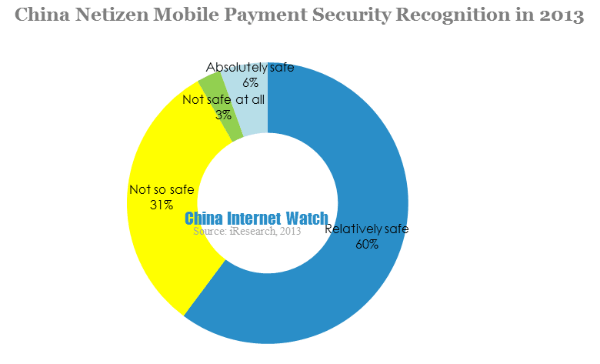
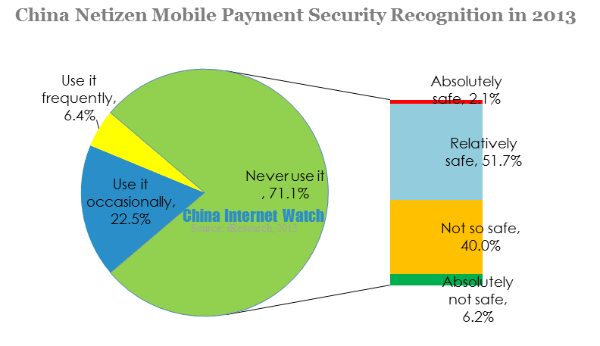
60.2% of Chinese mobile netizen regarded mobile payment safe, only 31.5% and 2.8% thought mobile payment “not so safe ” and “not safe”. Even among users who hadn’t use mobile payment before, half of them thought mobile payment was safe.
Mobile payment security recognition was due to technology and law protection, also due to user experience. With technology and law improvement, mobile payment security gained wide recognition. Still, occasionally, there were security loopholes which led to part of users felt unsafe.
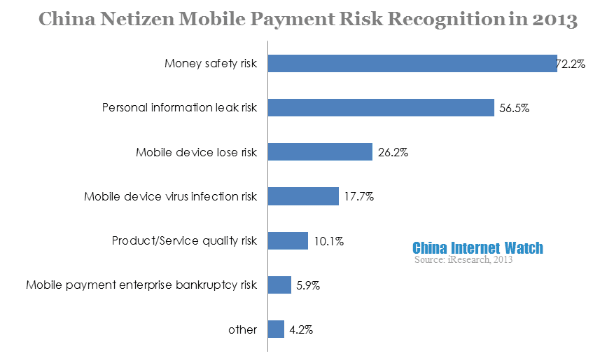
Top two risks in mobile payment were money safety risk and personal information leak risk. These were the most urgent needs of mobile users and the most difficult problems to solve.
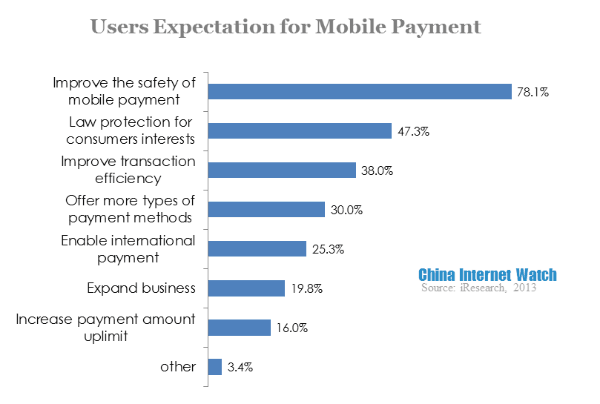
78.1% of mobile netizen expected to improve mobile payment security. Users had greater demands to satisfy their personal interests than improving mobile payment itself. Security became the crucial part of mobile payment user experience.
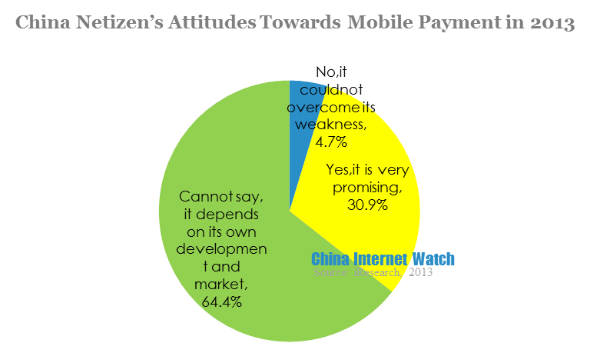
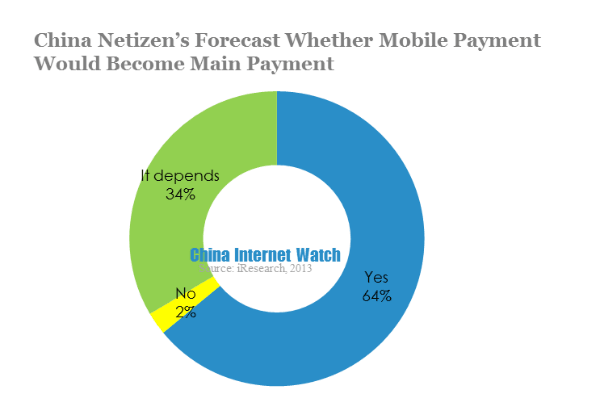
30.9% of mobile netizen were optimistic that mobile payment would be the main payment method in the future, while 64.4% of users were more reserved. 64% said they would use mobile payment, only 2.5% said they would not use.
Mobile payment grew more popular as mobile internet and m-commerce developed, but mobile users needed to be guided and their using habits needed to be cultivated.