
Xiaomi filed an initial public offering (IPO) in Hong Kong on May 3, 2018, becoming the first technology corporation to use Hong Kong’s new rule, i.e. dual-class shares, for going public.
The filing is expected to raise at least US$ 10 billion and value the company at between US$100-120 billion, making it the largest IPO since Alibaba in New York.
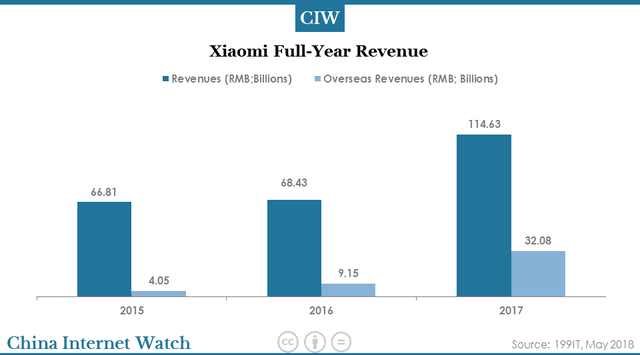
According to the IPO filing, Xiaomi’s revenue grew 167.5% from 68.43 billion yuan in 2016 to 114.64 billion yuan in 2017.
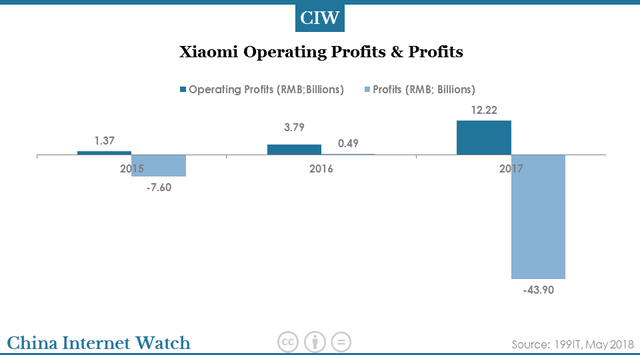
Xiaomi’s operating profits reached 12.22 billion yuan in 2017, an increase of 222.7% year-on-year. Xiaomi made a net loss of 43.9 billion yuan in 2017, down from 0.49 billion yuan profit a year earlier.
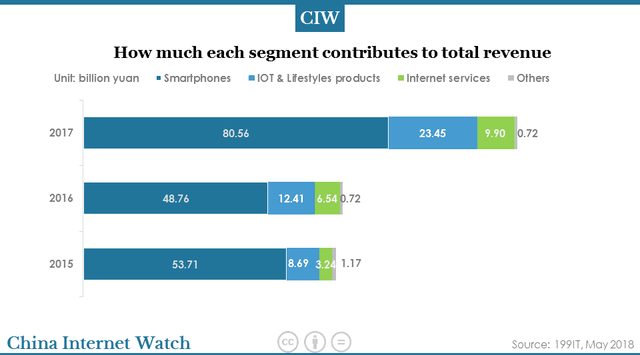
In 2017, Xiaomi derived nearly 70.3% of its revenue from smartphones, which was 80.56 billion yuan. Revenue derived from IOT (internet of things) and lifestyle products reached 23.45 billion yuan, accounting for 20.5% of the total. Revenue derived from internet service was 9.9 billion yuan, accounting for 8.6% of the total.
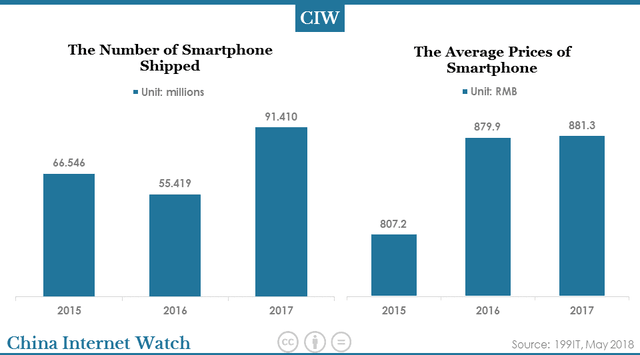
In terms of sales volume and average selling prices of Xiaomi smartphone, Xiaomi sold 66.546, 55.419, and 91.41 million smartphones respectively from 2015 to 2017. The average selling price of a Xiaomi smartphone was 807.2 yuan, 879.9 yuan, and 881.3 yuan respectively from 2015 to 2017.
As of 31 March 2018, Xiaomi has developed 38 10-million-MAU and 18 50-million-MAU mobile apps including Xiaomi App Store, Xiaomi Browser, Xiaomi Music, and Xiaomi Videos. On average, a Xiaomi user spends about 4.5 hours on the smartphone.
Check out China mobile app user insights 2018